Lead acid batteries and lithium batteries are the most common in car batteries. Lead acid batteries are mainly used in cars that run on petrol and diesel. Lithium batteries are mainly used in electric and hybrid vehicles. Lead acid batteries account for a large proportion of car batteries. This time, in this Blog, we will introduce you about how to improve the performance of your lead acid batteries.
Classification of Lead Acid Batteries
Lead acid batteries are also known as SLI batteries. It’s described in terms of what they can do, meaning starting, lighting and ignition. They can be mainly divided into wet batteries and valve regulated lead acid batteries (VRLA). Wet batteries can also be called flooded batteries, while VRLA batteries can also be called sealed lead acid batteries. The interior of a wet battery consists mainly of lead plates and electrolyte. A wet battery needs to be replenished with distilled water or deionized water regularly to maintain a reasonable electrolyte level. The advantage of VRLA batteries is that they are basically maintenance-free. They are safer than wet batteries. But they usually cost more. In VRLA batteries, the most common ones are AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries. They are of good quality. Compared with ordinary lead acid batteries, they can provide higher performance in a short time.
How Long Will Lead Acid Batteries Last?
Lead acid batteries are charged and discharged by the chemical reaction between the metal lead and the electrolyte, which is mainly diluted sulfuric acid. So the service life of these batteries is often closely related to how they are used and maintained. Proper use and maintenance Let Lead Acid Batteries Work Better. Normally, wet batteries can last about five years if they are properly maintained. VRLA batteries, on the other hand, tend to last longer than wet batteries, often up to five to 10 years. This is owing to their higher quality and thicker lead sheet materials used in their manufacturing process.
Influence of Temperature on Lead Acid Batteries
The chemical reaction in a lead acid battery depends on the ambient temperature. The optimum working temperature for both wet and VRLA batteries is around 25℃. Whether in hot or cold environment, both high and low temperature will affect the battery’s life span. If the temperature is too high, the electrolyte inside the battery tends to evaporate more. When it is too cold, the activity of the electrolyte also decreases. Both evaporation of the electrolyte and decreased activity will to some extent reduce the capacity of the battery. It has even been calculated that at very low temperatures, the capacity of lead acid batteries may drop by nearly 50%.
How to Solve the Corrosion Problem in Electrodes?
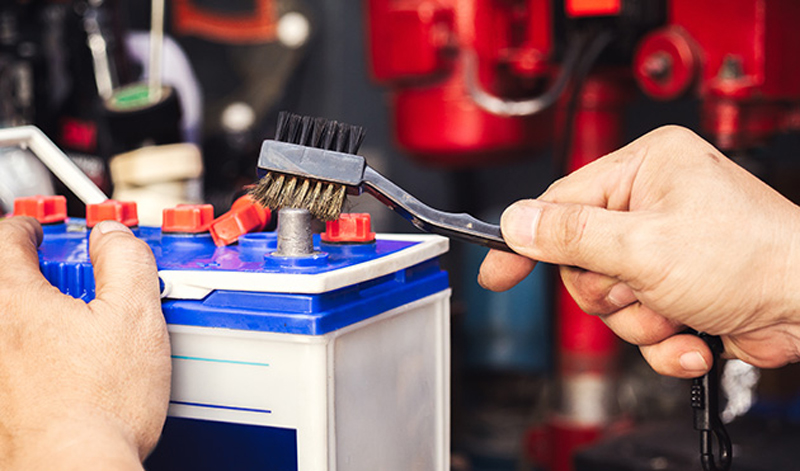
After a period of use, what we can see from a lead acid battery is that its electrodes might have been corroded. The cause of such corrosion is lead oxides. Long-term accumulation of such lead oxides can lead to poor contact between the battery and the wire and reduced output voltage. These lead oxides can be removed by using a small amount of alkali, salt, a dilute solution of washing powder, or dilute sulfuric acid. In addition, the corrosion problem of this place needs a regular inspection to ensure a good connection between the cable connectors and the terminal posts.

Causes of the Degradation of Lead Acid Battery Performance
In the daily use of the cars, the power in lead acid batteries is basically replenished by the car’s alternator. The alternator continuously recharges the battery while the vehicle is running on the road. But the normal charging process can be disrupted by a number of factors which can easily drain the battery. The most common causes of unexpected battery draining are the following two:
1. Sulfation of Lead Acid Batteries
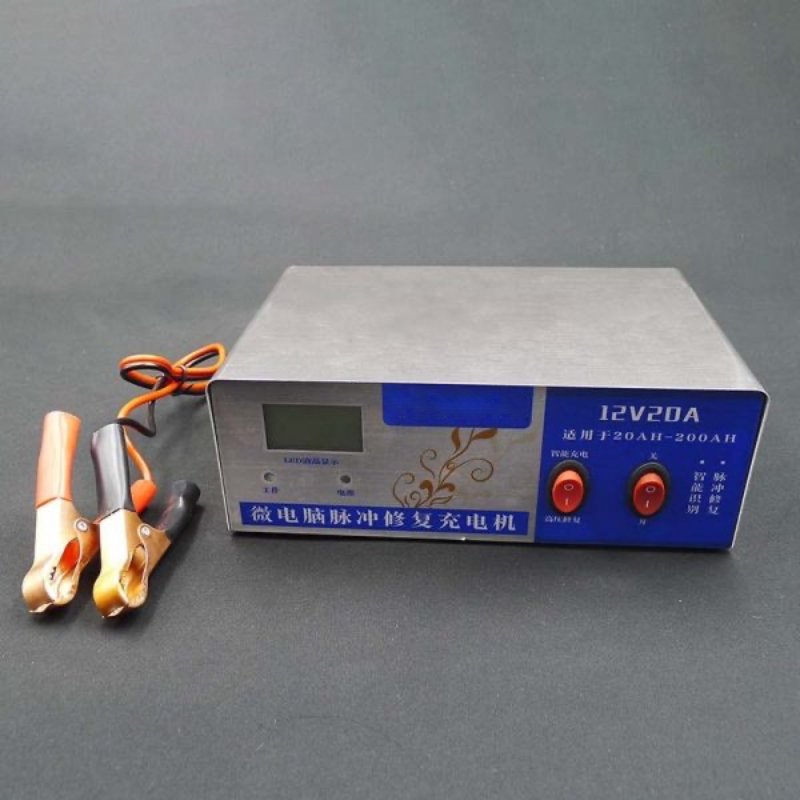
Sulfation of lead acid batteries is one of the main causes of the sudden drop in battery capacity. And such sulfation is mainly caused by excessive discharge of the battery. If the battery has been over discharged for a long time, the sulfation problem can be terrible. Sulfation problem of lead acid batteries cannot be resolved by the daily use of the battery or the vehicle. But it can be properly handled by using battery repair devices such as a Microcomputer Pulse Repair Battery Charger.
2. Frequent Short Distance Driving
Frequent short distance driving can also cause a sudden drop in lead acid battery capacity. Frequent start-ups will deplete the battery while short distance driving cannot give enough time for the battery to recharge. Therefore, frequent short distance driving can lead to a degradation of the lead acid battery performance.
Why Lead Acid Batteries Can’t Be Recharged?
In the daily use of lead acid batteries, sometimes they might not be recharged normally. And sometimes even though they have been fully recharged, they cannot hold the power properly. There are many reasons for the above situations, but the most common ones are in the following:
1. Something has been constantly consuming the power
One cause of a dead lead acid battery is that the lights or other electric devices in a car may be left on when the driver leave the car. If so, they will surely accelerate the consumption of the power in the battery. To make sure whether it is the problem that caused the drop in the battery power, remove the battery and charge it with a car battery charger. And then put it back into the car and see if the battery can hold its power over the next few days.
2. Problem in the alternator
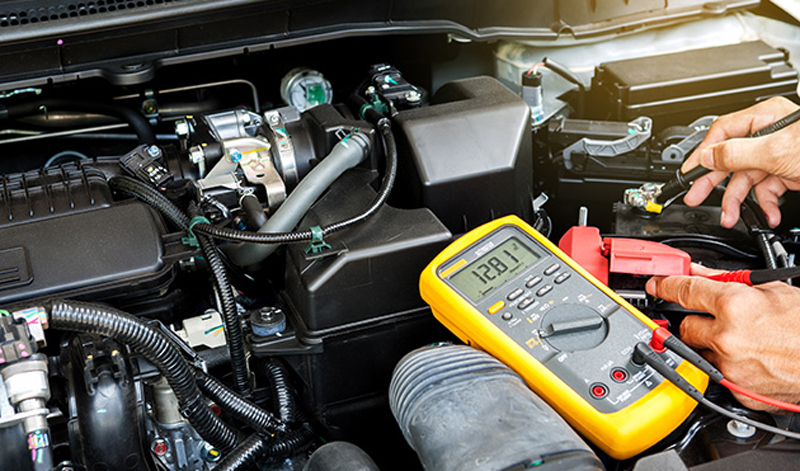
Lead acid batteries that don’t charge or store power properly could also be an alternator problem. The alternator is responsible for recharging the battery and powering other electrical devices while the engine is running. To judge whether this is the case, a multimeter can be used to measure the output voltage of the alternator. The normal output voltage of an alternator should be between 13.8 and 14.4V. If the voltage measured is outside this range, check to see if the alternator is faulty.

3. Other factors
The corrosion of the electrodes of a lead acid battery can lead to a poor contact between the wire and the battery or a drop in its capacity. Sometimes this can be mistaken for a battery capacity problem. Therefore, regular inspection and cleaning of the electrodes can also help to reduce the likelihood of battery problems.