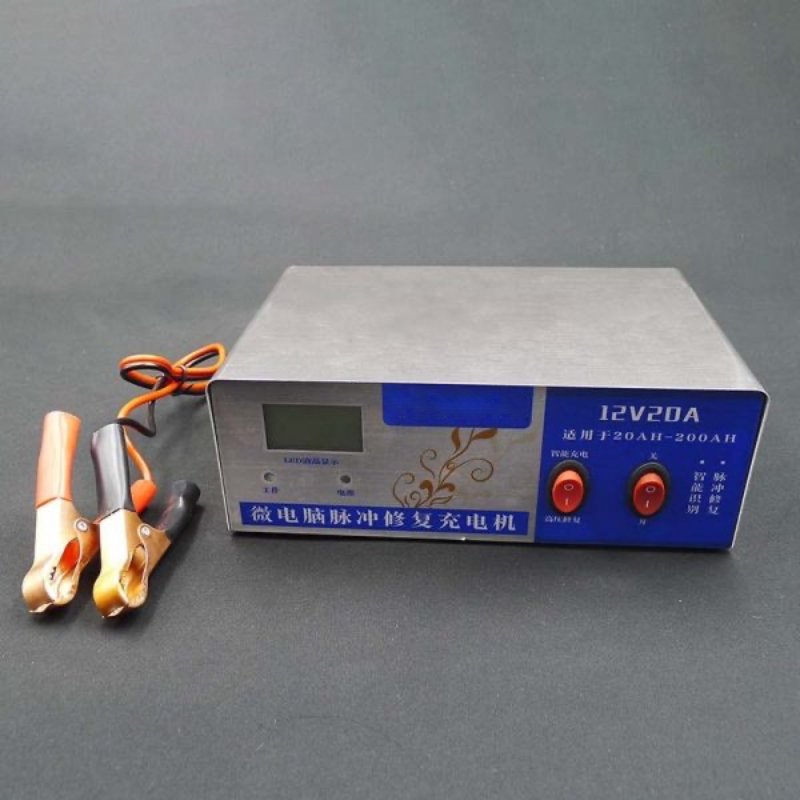
Car battery chargers and jump starters are common to see in the daily use of cars. For these two, not all people can tell their differences. Are they functionally interchangeable? Today, we’ll compare the two and find out how they differ with each other in this blog.
Car Battery Chargers
Like our laptop or cell phone chargers, car battery chargers are used to charge car batteries. A household electrical outlet produces 120 volts of alternating current, while a car battery needs 12 volts of direct current. Therefore, either from the voltage or the interface, a car battery cannot be directly connected to a household socket. The charger’s role is to achieve the conversion between the two currents. When in use, one end of the charger is connected to a home socket through a plug, while the other is connected to the electrodes of the lead acid battery through two clips.
Like chargers of electronic products, car battery chargers provide a steady current to charge the battery. They can charge the battery when it is dead and maintain the battery when it is fully charged. Different chargers are in different electric power levels, which can reflect the level of electric current and speed of their charging process. The battery voltage is usually between 6 and 24V, and the vast majority of cars use 12V batteries. Charging voltage of the battery should be known when choosing a battery charger for a car. Improper chargers can cause irreversible damage to the battery, and even cause danger.
Car battery chargers provide a constant and steady charging current to the battery. Such current is not as strong as that of a jump starter that we’ll talk about later, but they’re useful for long-term battery use and maintenance. Nowadays, many car battery chargers also have pulse repair functions. They can be used both for battery charging and the recovery of battery capacity, from which malfunctioned batteries can be restored to life.
In terms of working hours, it usually takes several hours to recharge a battery with a car battery charger. So, if you run into a battery problem in a time-sensitive morning, they tend not to be very helpful.
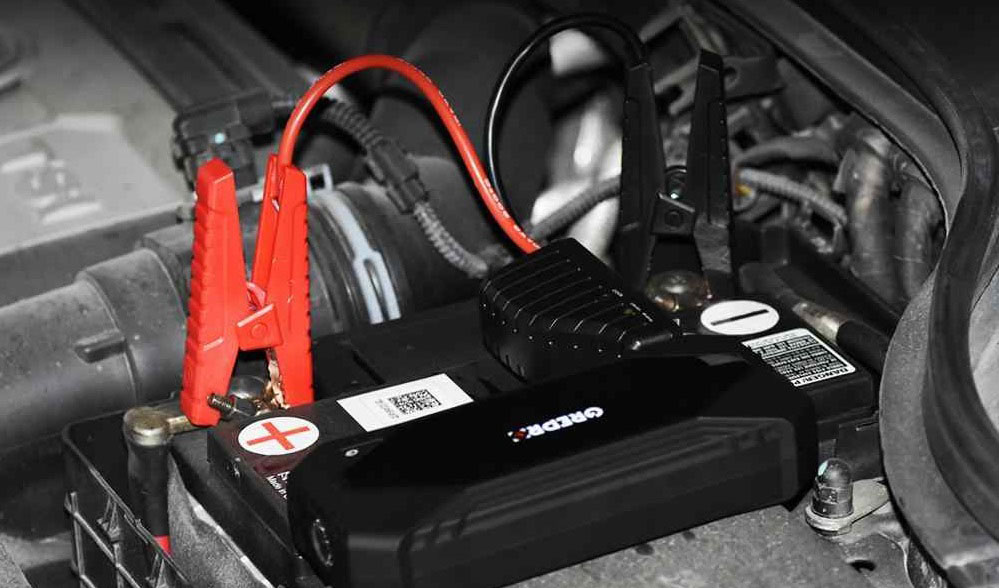

Jump Starters
Compared with a battery charger, a jump starter is a portable battery pack. They are mainly used to start a car in case of battery problems. They come with a 12V DC output for cars and can be connected to the battery via a specialized jumper cable to supply power to the battery.
While a battery charger mainly does the charging work, a jump starter can help to start a vehicle quickly if the battery fails to. Once the car is started, its own alternator will charge the battery as it travels.
A jump starter will be useful when a vehicle encounters a battery problem on the road. They are also portable and can easily fit under the seat or in the trunk of the vehicle. Many jump starters also come with USB ports for charging other gadgets like cell phones.
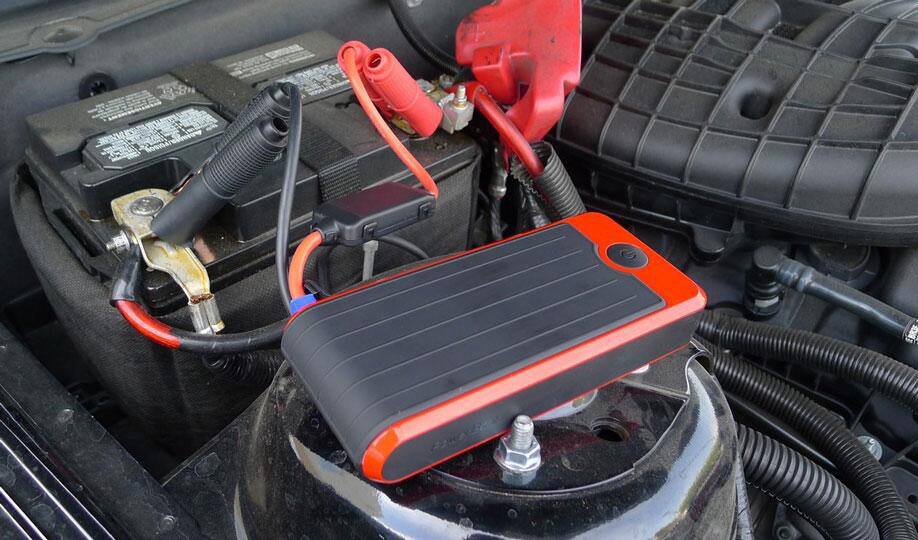

Summary
From the above introduction of these two types of products, we can easily see the differences between the two just from their names. Battery chargers are used to charge car batteries. Some products can also have battery repair and recovery functions. Jump starters come with their own built-in batteries. They can be regarded as portable emergency starting batteries. They are mainly used to start the vehicle in case of battery problems. They can solve vehicle starting problems more quickly than battery chargers, but they can’t be used for battery recharging or repair.
FAQ
- Q: What can car battery chargers and jump starters do and cannot do respectively?
A: Car battery chargers are used to charge the battery, and the charging time is determined by the battery capacity and the charging power of the charger. Some battery chargers also have pulse repair functions that can repair faulty batteries. A car battery charger cannot realize emergency start of a vehicle in the case of a battery failure. Jump starters cannot be used to charge car batteries. Their function is to provide an instant powerful flow of current that is enough to start the vehicle. The battery will then be charged by the car’s own alternator in the driving process. - Q: Can a battery be charged while it is still attached to the car?
A: Yes, but for safety, try not to do this. - Q: Can I just keep a battery charger working at night?
A: It depends both on the battery and charger since there is a risk of overcharging. Some battery chargers can prevent the battery from being overcharged with their automatic shut off function when the battery is fully charged, so there will be no risk to the battery. But not all chargers have such function to turn themselves off. Battery chargers without automatic shut off function may cause permanent damage to the battery, or even cause leakage of electrolyte or explosion. For a battery charger without automatic shut off function, if you can ensure that it takes a night time to charge the battery by referring to the parameters of the charger and the battery, then you can keep the charger on at night. This can be done if the charger will be timely disconnected from the battery when it is fully charged. - Q: How to calculate the charging time of a battery?
A: The charging time of a battery depends on the capacity of the battery and the outlet of the charger. The time required to charge a battery is roughly equal to the capacity of a battery divided by the outlet of the charger. A typical car battery has a capacity around 70 Ah. If a 6A battery charger is used to charge a 70 Ah battery, it will take about 12 hours to have it fully charged.