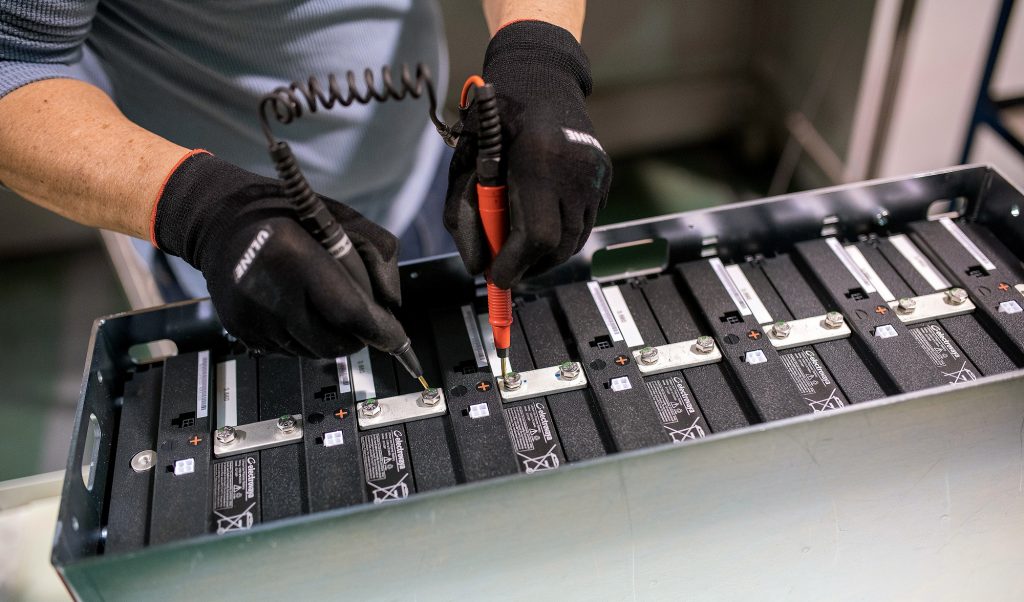
A lithium iron phosphate battery is one kind of li-ion battery which uses lithium iron phosphate as cathode material and carbon as cathode material. They offer higher capacity and power rate than previous traditional li-ion batteries. With a better performance, lithium iron phosphate batteries can not only be used as storage cells, but also as power battery sources. In this blog, we will give an introduction of its working principle, as well as the comparison with traditional li-ion batteries and lead acid batteries.
Working Principle
Like common li-ion batteries, lithium iron phosphate batteries rely on the movement of lithium ions between anode and cathode to work. When a battery is charged, some of the lithium ions in the lithium iron phosphate detach from the positive electrode and pass through the dielectric to the negative electrode, where they will be embedded in the carbon material. At the same time, electrons are released from the battery’s anode. The electrons travel through the external circuit to the negative electrode, thus maintaining the equilibrium of the chemical reaction. When a battery discharges, lithium ions will escape from the negative electrode and travel through the dielectric to the positive electrode. At the same time, electrons are released from the battery’s cathode. Electrons travel through the external circuit to the positive electrode, where they release energy.

Compare with Li-ion Batteries
Lithium iron phosphate batteries belong to the li-ion battery family. Compared with ordinary li-ion batteries, they are a new type.
First of all, li-ion batteries usually use LiCoO2 or LiMn2O4 as cathode material, while lithium iron phosphate batteries usually use LiFePO4. From the building material itself, lithium iron phosphate batteries are environment-friendly. Lithium iron phosphate is a non-toxic material that complies with European RoHS regulations, while LiCoO2 is considered hazardous.
Secondly, the cathode material in lithium iron phosphate batteries has a better thermal and chemical stability. So, the battery has a stable charge and discharge performance. This means that compared with li-ion batteries, lithium iron phosphate batteries are less likely to burn or explode in the event of improper handling. It is very safe even in the case of short circuit, overcharge, stabbing, etc.
In addition, the use of phosphate materials makes lithium iron phosphate batteries last longer. They are more stable than li-ion batteries in the event of overcharge or short circuit. The cycle life of li-ion batteries is about 400 times, while the cycle life of lithium iron phosphate batteries is generally 2,000 times, and some can even reach more than 3,500 times. Lithium iron phosphate batteries typically have a life span of 8-10 years.

Compare with Lead Acid Batteries
Compared with lead acid batteries, lithium iron phosphate batteries have higher charging current, higher charging efficiency and faster charging speed.
A lead acid battery is an aqueous system. As a heavy metal, lead has an energy density about 35-40 Wh/kg. While as a non-aqueous system, lithium iron phosphate batteries have an energy density about 145 Wh/kg. So, lithium iron phosphate batteries have about 4 times the energy density of lead acid batteries. Meanwhile, lithium iron phosphate batteries of the same capacity are about 2/3 the size and 1/3 the weight of lead acid batteries.
Lead acid batteries typically have a cycle life about 300 times, which is a great contrast compared with about 2,000 times in lithium iron phosphate batteries.
Lithium iron phosphate batteries have no memory problem. Therefore, there is no need to consider having to completely drain them before charging them. They can be recharged at any time like cell phone batteries. They do not need to be charged in time after partially discharged either. So, they do not have the sulfation problem caused by delayed recharging in lead acid batteries.
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are easier to store than lead acid batteries since they have a very low self-discharge rate. Generally, there is no need to do any preparation work for their short-term storage about only 3-6 months. What you need to do is to maintain its power capacity at 50% before the storage. If they are for long-term storage, they need to be maintained a power capacity at 50% first, and then be charged, discharged and recharged once every 6 months.